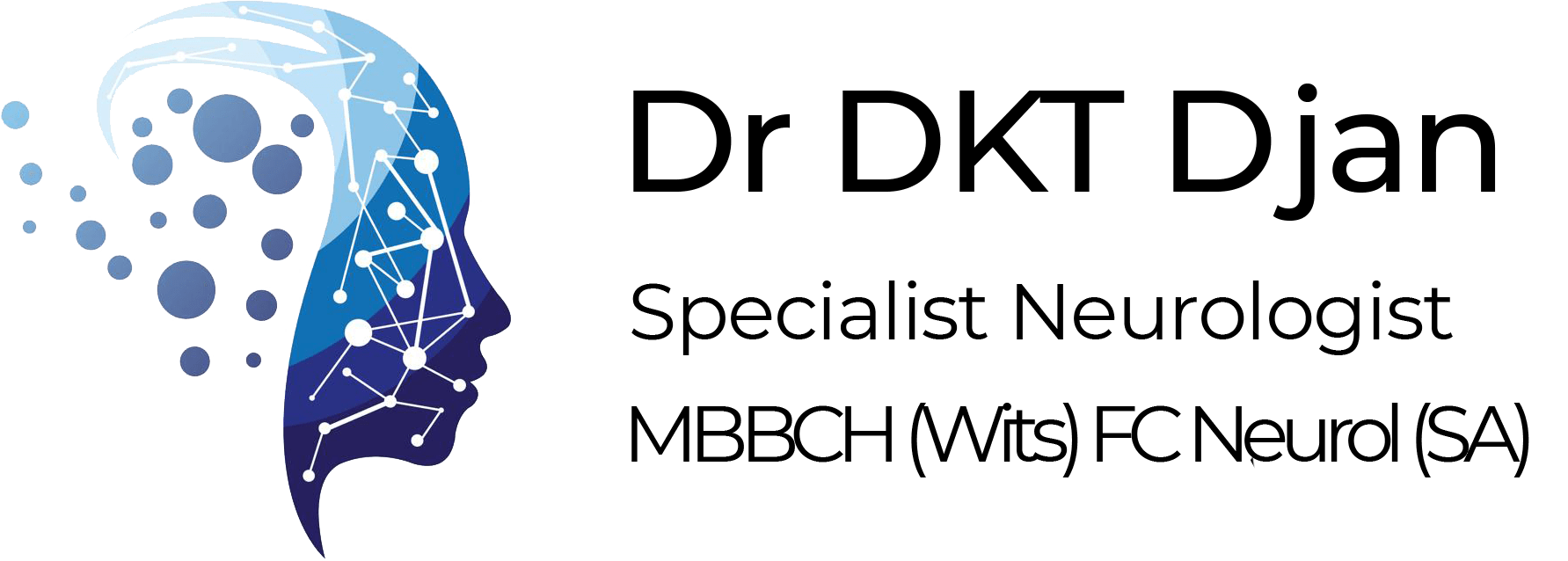

A stroke occurs when a blood vessel in the brain ruptures and bleeds, or when there is a blockage in the blood supply to the brain. The rupture or blockage prevents blood and oxygen from reaching the brain’s tissue. Without oxygen, brain cells and tissue can become damaged or even begin to die within minutes.
When someone is having a stroke, the sooner they get care, the better the outcome is likely to be. This is why it is so vital to know the signs of a stroke so you can act quickly.

There are certain risk factors that increase your chances of having a stroke. They include:
However, there are some risk factors that are out of your control, such as:
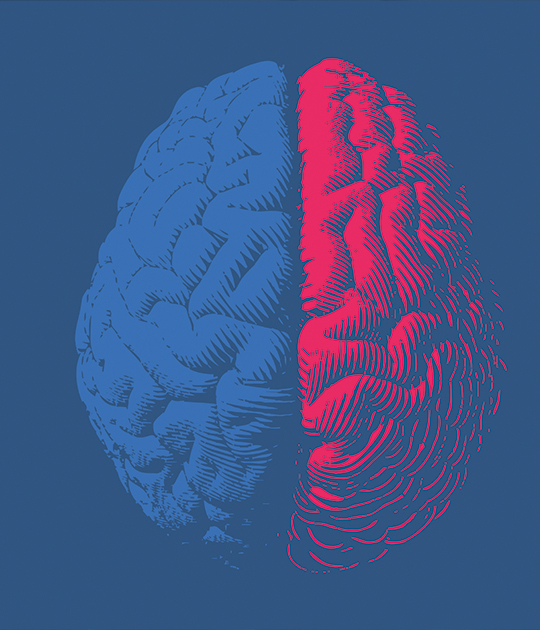

The effects of a stroke depend on the location of the obstruction and how much brain tissue was damaged. One side of the brain controls the opposite side so if a stroke occurs on the right side, it will result in neurological complications on the left side of the body.